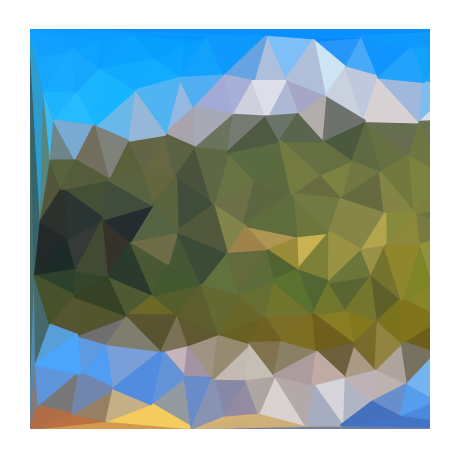
Technical Implementation
The algorithm uses Poisson disk sampling to generate well-distributed points, which are then used to create a triangular mesh via Delaunay triangulation. Each triangle in this mesh is filled with the average color of the corresponding area in the original image.
- Delaunay triangulation is a mathematical technique that maximizes the minimum angle of all triangles in a mesh. This creates a more aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound triangulation compared to other methods.
- Poisson disk sampling is a method for generating well-distributed points in a given area. It is often used in computer graphics and computational geometry to create realistic-looking patterns and textures.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
from matplotlib.collections import PatchCollection
from scipy.spatial import Delaunay, distance
def generate_poisson_points(width, height, n_points=2500, min_dist=20, n_trys=100, seed=None):
np.random.seed(seed)
# initialize
cell_size = min_dist / np.sqrt(2)
grid_width = int(np.ceil(width / cell_size))
grid_height = int(np.ceil(height / cell_size))
grid = np.full((grid_width, grid_height), -1, dtype=int)
points = []
active_list = []
x = np.random.uniform(0, width)
y = np.random.uniform(0, height)
points.append([x, y])
active_list.append(0)
grid_x, grid_y = int(x / cell_size), int(y / cell_size)
grid[grid_x, grid_y] = 0
# sample
while active_list and len(points) < n_points:
idx = np.random.choice(active_list)
base_x, base_y = points[idx]
for _ in range(n_trys):
angle = np.random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi)
d = np.random.uniform(min_dist, 2 * min_dist)
new_x = base_x + d * np.cos(angle)
new_y = base_y + d * np.sin(angle)
if 0 <= new_x < width and 0 <= new_y < height:
grid_x, grid_y = int(new_x / cell_size), int(new_y / cell_size)
if grid[grid_x, grid_y] == -1:
valid = True
for dx in [-1, 0, 1]:
for dy in [-1, 0, 1]:
nx, ny = grid_x + dx, grid_y + dy
if 0 <= nx < grid_width and 0 <= ny < grid_height:
if grid[nx, ny] != -1:
px, py = points[grid[nx, ny]]
if distance.euclidean([new_x, new_y], [px, py]) < min_dist:
valid = False
break
if not valid:
break
if valid:
points.append([new_x, new_y])
active_list.append(len(points) - 1)
grid[grid_x, grid_y] = len(points) - 1
break
if _ == n_trys-1:
active_list.remove(idx)
return np.array(points)
# poisson disk sampling
points = generate_poisson_points(width, height, seed=1)
points = np.vstack([points, [[0, 0], [0, height], [width, 0], [width, height]]])
tri = Delaunay(points)
# create polygons for each triangle
polygons = []
img_array = np.array(img.rotate(-90, expand=True))
for simplex in tri.simplices:
# calculate average color within the triangle
polygon = Polygon(points[simplex], closed=True)
mask = polygon.get_path().contains_points(np.array(list(np.ndindex(width, height))))
mask = mask.reshape(width, height)
if not np.any(mask):
continue
# set the color of the polygon
avg_color = np.mean(img_array[mask], axis=0) / 255.0
polygon.set_facecolor(avg_color)
polygon.set_edgecolor(avg_color)
polygons.append(polygon)
# plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(width/100, height/100), dpi=100)
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0, right=1, top=1, bottom=0, wspace=0, hspace=0)
ax.add_collection(PatchCollection(polygons, match_original=True))
ax.set_xlim(20, width-20)
ax.set_ylim(0, height)
ax.axis("off")
plt.show()